Data Stores
Overview
Data Stores provide a layer of abstraction between the working WC_Data object and the information stored in the database. In understanding how they work, you’ll know what your objects are doing when they create, load, save, and delete; and how to customize these behaviors. In this topic, we’ll cover:
Interfaces
- The WC_Object_Data_Store_Interface defines the methods required for a WC_Data object
- Each family of WC_Data (e.g. product, coupon, order-item, etc.) has it’s own interface to identify specific methods for that family’s data stores to operate reliably
- When implementing a custom data store, both WC_Object_Data_Store_Interface and the family-specific interface should be implemented.
- However, the WC_Data_Store class will only verify that the loaded datastores implement WC_Order_Data_Store_Interface. The constructor method of the WC_Data_Store class does an instanceof check (on line 94) Failure to use the family ‘assistant’ interfaces will not automatically throw an Error
Assistant Interfaces
- WC_Customer_Data_Store_Interface
- WC_Customer_Download_Data_Store_Interface
- WC_Customer_Download_Log_Data_Store_Interface
- WC_Object_Data_Store_Interface
- WC_Order_Data_Store_Interface
- WC_Order_Item_Data_Store_Interface
- WC_Order_Item_Product_Data_Store_Interface
- WC_Order_Item_Type_Data_Store_Interface
- WC_Order_Refund_Data_Store_Interface
- WC_Payment_Token_Data_Store_Interface
- WC_Product_Data_Store_Interface
- WC_Product_Variable_Data_Store_Interface
- WC_Shipping_Zone_Data_Store_Interface
- WC_Webhook_Data_Store_Interface
Interface Methods
- Notice that each method in the interface receives the Data Object $data, which is passed by reference. In implementation this is an instantiated object, such as a product, or order item
- Consequently each $data_store directly edits it’s $data object with database information
- This is primarily used so that the data store can easily set_props in the WC_Data object as it interacts with the database

Data Store methods
| WC_Data object method | Data Store method |
|---|---|
| __construct($id | $object) | read($data) |
| save() | create($data) update($data) |
| delete($force_delete) | delete($data, $args) |
| read_meta_data() | read_meta($data) |
| save_meta_data() |
delete_meta($data, $meta) add_meta($data, $meta) update_meta($data,$meta) The data_store uses WC_Meta_Data to assess which methods are necessary and minimize database transactions |
WC_Data_Store_WP: The Fundamental Default Data Store Class
- WC_Data_Store_WP is a foundational class but it’s use is not requiredThe generic parent class for a CPT data object’s data store
- The WC_Data_Store_WP class does NOT fully implement the WC_Object_Data_Store_Interface Meaning, you must add the interface methods after you extend it.
- It provides methods for using WordPress’s custom post types, metadata, taxonomy, WP_Query, and Search APIs
- Descendants of WC_Data_Store_WP override this functionality as necessary (e.g. the Abstract_WC_Order_Item_Type_Data_Store)
WC_Data_Store_WP Properties
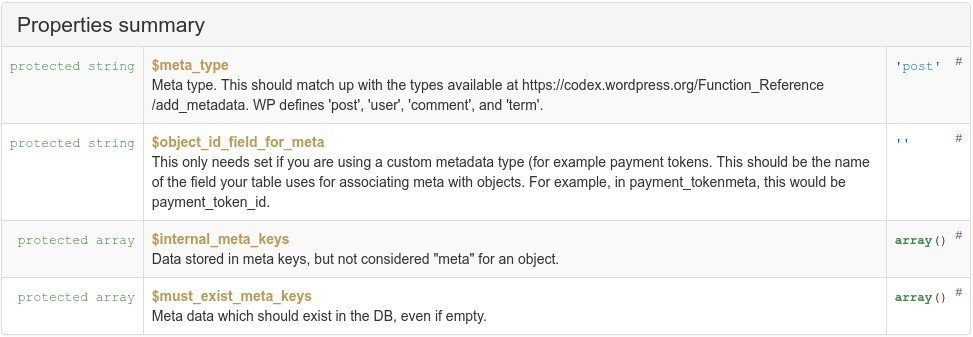
WC_Data_Store_WP lookup tables
- Lookup tables provide a mechanism for improving read and write efficiency over typical meta tables
- The WC_Product_Data_Store provides an example of this in the wc_product_meta_lookup table
- Key methods supporting this feature are:
- get_data_for_lookup_table( $id, $table) Note: this returns an empty array in the foundational class
- get_primary_key_for_lookup_table($table) Note: this returns an empty string in the foundational class
- update_lookup_table($id, $table) By implementing the above two methods, the update and delete methods will function
- delete_from_lookup_table($id, $table)

Structure of the wc_product_meta_lookup table.
Conclusion
Now that you know the interfaces that define data stores, and how the data store methods map to the WC_Data methods, you should feel more confident in your ability to navigate transactions between WC_Data object and the database. These two concepts are the keys to creating your own data stores, and fully customizing a WC_Object’s behavior.
Next, we’ll take a quick tour of each of the WC_Data families.
But first, check your knowledge.
Knowledge Check
Hint: You can use CTRL+Shift+F to quickly search the slides for information.
Quiz Summary
0 of 3 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 3 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 3
1. Question
WC_Data_Store_WP is a…
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 3
2. Question
Data Stores receive what argument for all standard methods?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 3
3. Question
Lookup Tables Are…
CorrectIncorrect
Keyboard shortcuts
Down arrow Next slide
Up arrow Previous slide
Color codes
Hover over text more additional info